Aquaculture is basically the practice of farming aquatic animals and plants. Aquatic animals include fishes, crustaceans, mollusks, and other organisms such as carp, trout, freshwater crayfish, clams, and oysters. Besides, it also involves algae and other plants such as seaweeds.
This form of farming can take place in more than one kind of environment. Though it is common in freshwater and marine water sources, it can also be practiced in brackish water.
Aquaculture takes place under controlled conditions. Though it sounds similar to commercial fishing and mariculture, it is distinct from both. These methods constitute the subsets of the farming method in question. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines its scope to mark a line of distinction for it from other farming practices.
Aquaculture corresponds to intervention in the process of breeding and looking after aquatic animals. As much as it is about increasing the production of aquatic plants and animals, it is also about providing food to them. Besides, it is also about offering protection to them from predators that endanger their existence.
Aquaculture Forms
MSD Aquaculture prides itself in adopting the best practices of aquaculture for its following forms:.-
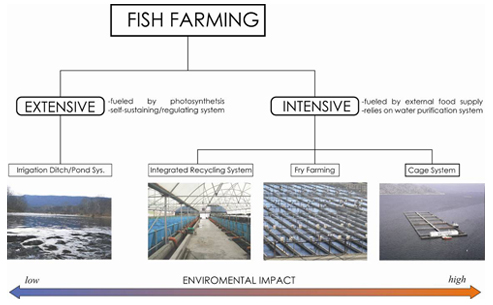
Intensive Production
It involves the farming of a larger population of aquatic organisms and their regular feeding..
-
Semi-Intensive System
It refers to the farming of a relatively lesser population of aquatic plants and animals and feeding them with naturally occurring foods.
-
Extensive Aquaculture
Also practiced with a lower density of aquatic organisms, this approach is about providing food to aquatic organisms from naturally occurring food sources in a controlled environment.
Current Scenario (India & Abroad)
India occupies one of the top positions when it comes to the consumption of fishes. Fish farming in India and its growth in the last few years has been a major contributor to it. Not only has it helped increase the production of fishes but also enhanced its quality for the consumption of fishes as one of the chief sources of food.
While the production of fishes from aquaculture suits well for consumption in India, it also generates income for local households in the country. Apart from providing work to those involved in mainstream activities, the practice of fish farming also creates employment opportunities for individuals in the form of support activities.
Freshwater and brackish water fish farming form the backbone of aquaculture in India. Thus, it is vital to focus on sustainable development in this sector. This way, the growth engine of the sector can gather steam without compromising the safety of the environment.
The best part about the growth of fish farming in the last few years is that despite the addition of modern methodologies and approaches to it, it has been on the path of sustainable growth. This presents brighter prospects for the future of fish farming in the years to come, not only for India but worldwide.
Future Scope (India & Abroad)
India has a wide range of water sources that make it conducive for aquaculture. The diversity of fish species also complements the impressive array of water bodies for this purpose. Aquaculture makes a significant contribution to the growth of the Indian economy every year.
In the past, traditional methods of fish farming were largely in practice. However, these modern methods of fish farming are fast replacing the old practices nowadays. A greater emphasis on the application of modern methodologies has helped attract the attention of farmers who view aquaculture favorably now than ever before.
Not only has aquaculture helped utilize the under-utilized lands and water resources for productive purposes, but it has also paved the way for the best method of waste management. Waste released by fishes in ponds and other water bodies is used for the fertilization of crops to improve the quality of crops.
If current trends are anything to go by, then a significant breakthrough can be expected in the coming years. As much as India looks at the global players to get the inspiration for the growth of its aquaculture sector, the converse is also true. This maximizes the scope for collaboration at the global level. Collective efforts of India with the other major players of aquaculture will be important to modernize the methodologies, sustain growth, and address the existing challenges.